If X and Y are two variates connected by the relation Y =aX+b/c and Var(X) = σ^2, then write the expression for the standard deviation of Y. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest

Probability: Prove that Var(aX+bY)=a^2 Var(X)+2ab Cov(x,Y)+b^2 Var(Y) where a & b are two costants - YouTube
![Let c be a constant. Using Var(X) = E [(X− E [X])^2 ], show that (a) Var(c X) = c^2 Var(X); (b) Var ( c+X) = Var(X). Let c be a constant. Using Var(X) = E [(X− E [X])^2 ], show that (a) Var(c X) = c^2 Var(X); (b) Var ( c+X) = Var(X).](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q6605.png)
Let c be a constant. Using Var(X) = E [(X− E [X])^2 ], show that (a) Var(c X) = c^2 Var(X); (b) Var ( c+X) = Var(X).

SOLVED: (a) Let X, Xz-X and %YzrY be random variables and let &."2' a and bbzb be constants. Prove that cov(X,Y) = ab * cov(X,Y). (b) Hence or otherwise, show that if
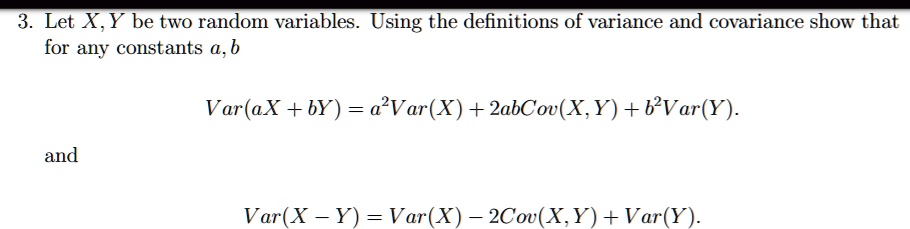
SOLVED: Let XY be two random variables. Using the definitions of variance and covariance, show that for any constants a and b: Var(aX + bY) = a^2Var(X) + 2abCov(X,Y) + b^2Var(Y) and

Express the following linear equations in the form ax + by + c = 0 and indicate the values of a, b and c in each case:(i) 2x + 3y = 9.3

SOLVED: Let a = 2 b = 1 c = -2 Var(X) = 1 Var(Y) = 2 Var(Z) = 3 Cov(X,Y) = -2 Cov(X,Z) = 1 Suppose Var(aX + bY + cZ) = 34. Find Cov(Y, 2).

SOLVED: Let: a = 2 b = 1 c = -2 Var(X) = 1 Var(Y) = 2 Var(Z) = 3 Cov(X,Y) = -2 Cov(X,Z) = 1 Suppose Var(aX + bY + cZ) = 34. Find Cov(Y, Z).



![Solved A) Which of the following is equal to E[aX+by+c]? | Chegg.com Solved A) Which of the following is equal to E[aX+by+c]? | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/bf5/bf5e87a3-d116-4e5b-8bcc-e15539fe86fd/phpHeIz3q.png)



![Given E(X + 4) = 10 and E[(X + 4)²] = 116, determine (a) Var | Quizlet Given E(X + 4) = 10 and E[(X + 4)²] = 116, determine (a) Var | Quizlet](https://d2nchlq0f2u6vy.cloudfront.net/18/10/08/ac6d46df86d829fecdb4772c7e8c7780/ba6bc202eb234e4da819ff84079a8474/lateximg.png)
![Given E(X + 4) = 10 and E[(X + 4)²] = 116, determine (a) Var | Quizlet Given E(X + 4) = 10 and E[(X + 4)²] = 116, determine (a) Var | Quizlet](https://d2nchlq0f2u6vy.cloudfront.net/18/05/26/3499b89e2973a13e130169cb0948f754/1116d4072bce6e95cbaf60198c5f09ed/lateximg_large.png)


