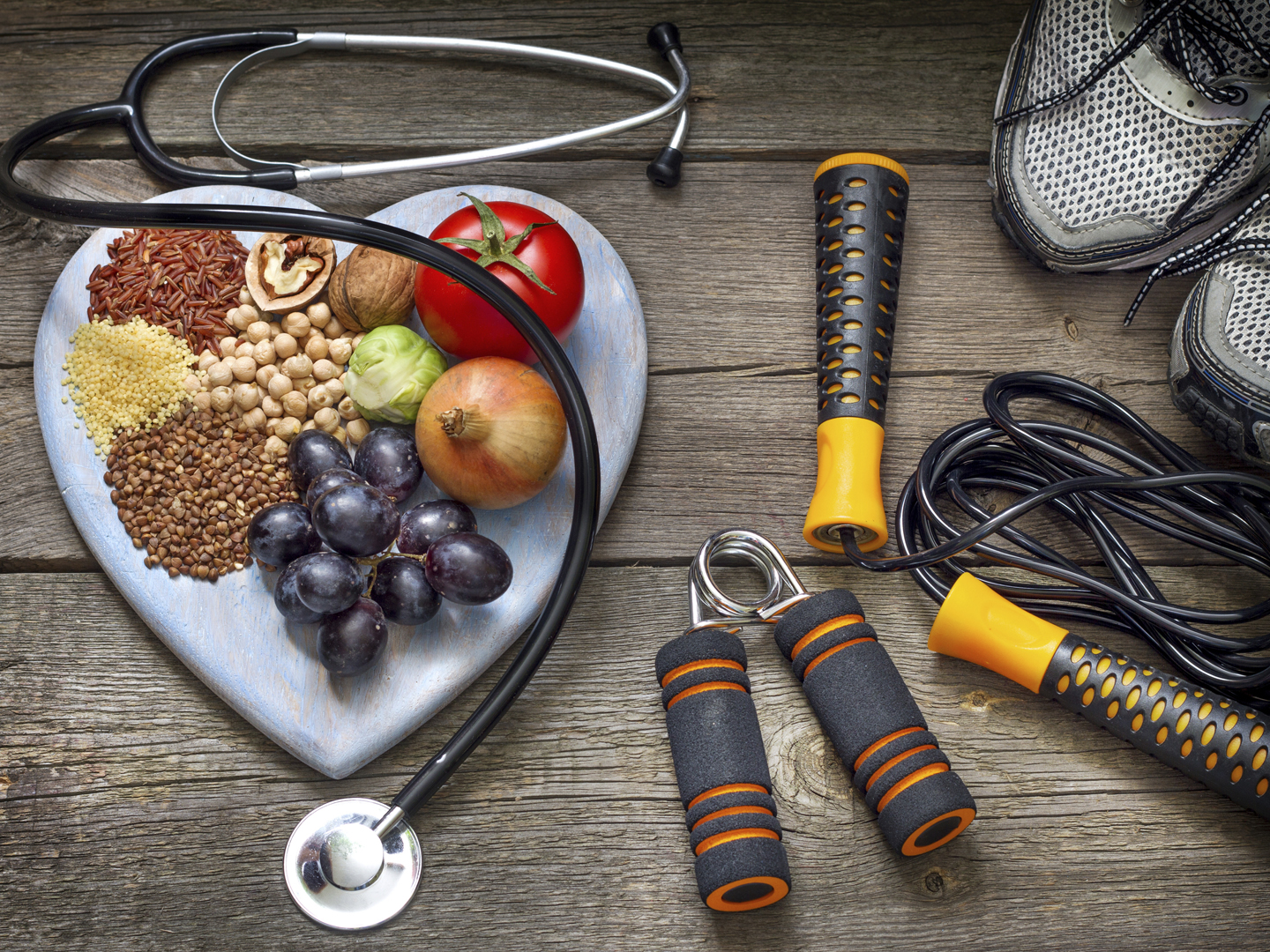
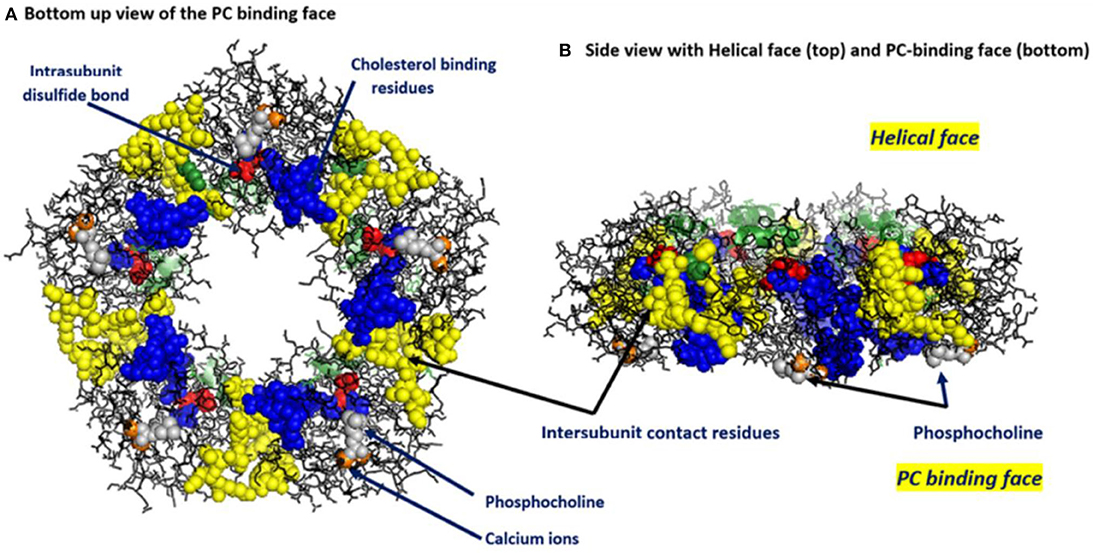
FIGURE 9.47, Prevalence of C-Reactive Protein ≥10 mg/L, by Diabetes Status and Age, U.S., 2005–2010 - Diabetes in America - NCBI Bookshelf
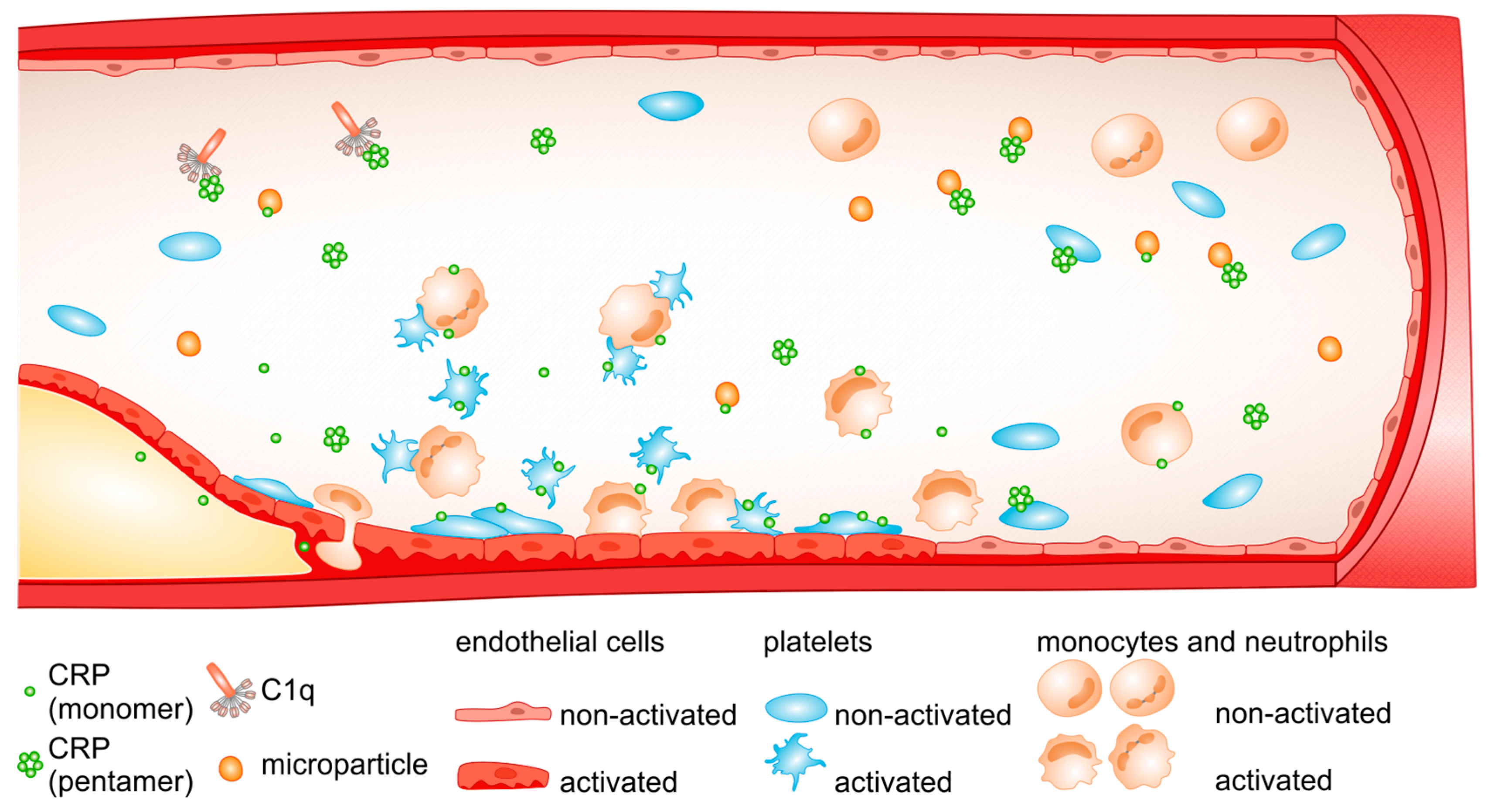
Molecules | Free Full-Text | The Multiple Faces of C-Reactive Protein—Physiological and Pathophysiological Implications in Cardiovascular Disease
![Figure 12, [Risk Ratio of CHD Associated with C-Reactive Protein (1.0 – 3.0 mg/L vs <1.0 mg/L)]. - Screening for Intermediate Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease - NCBI Bookshelf Figure 12, [Risk Ratio of CHD Associated with C-Reactive Protein (1.0 – 3.0 mg/L vs <1.0 mg/L)]. - Screening for Intermediate Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK35214/bin/es73.resultsf10.jpg)
Figure 12, [Risk Ratio of CHD Associated with C-Reactive Protein (1.0 – 3.0 mg/L vs <1.0 mg/L)]. - Screening for Intermediate Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease - NCBI Bookshelf

FIGURE 31.10, Mechanisms Underlying the Associations Between Periodontitis and Hyperglycemia/Diabetes and Its Complications: Conceptual Model - Diabetes in America - NCBI Bookshelf

Tony Breu on X: "8/ To understand why albumin is a negative acute phase reactant (APR), it is first helpful to review the role of positive APRs. I'll cover two key examples:
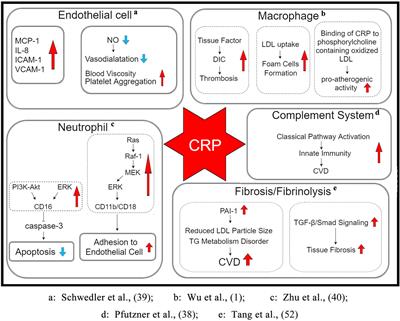
Frontiers | The Clinical Significance and Potential Role of C-Reactive Protein in Chronic Inflammatory and Neurodegenerative Diseases